Impact and correlation of pKa and dn electrons of some selected thiosemicarbazone Schiff base metal Co, Ni, Cu complexes: a study of electrochemical behavior, excitation and optical energies
Abstract
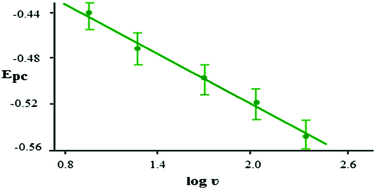
The electron-transfer and coordination mechanism of Schiff bases with metal ions, correlation of the electrochemical and optical properties for their potential applications in various fields of chemistry and biochemistry are underexplored. Thus, detailed assignment of the redox behavior of some Co2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ thiosemicarbazone complexes in tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate (TBA+BF4−)–dimethylformamide (DMF) was investigated by bulk cyclic voltammetry and controlled potential coulometry. The redox behavior of the electrode couples (M+/M2+ and M2+/M3+, M = Co, Ni or Cu) was dependent on the electron-donating (or withdrawing) substituent on the thiosemicarbazone moiety (N1H and/or N4H), pKa of the Schiff base, and dn electrons of metal ions. Upon increasing the concentration of the complex species in (TBA+BF4−)–DMF, the cyclic voltammograms of the complexes showed no significant variations in the values of the diffusion coefficient (D) (0.27–0.29) × 10−6 cm2 s−1. The Epa and Epc of selected electrode couples were satisfactorily correlated with the remote effect of N1H and N4H substituents, Hammett parameters (σ) and dn electrons of the metal ions. The optical band energies, HOMO and LUMO were obtained from electronic spectra and cyclic voltammograms, respectively. The mechanism describing the electron transfer of the electroactive species and stability of the complex species towards oxidation (M3+) and/or reduction (M+) was discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...