DBA-induced caspase-3-dependent apoptosis occurs through mitochondrial translocation of cyt-c in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
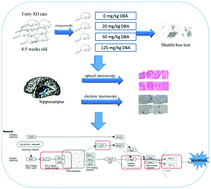
Dibromoacetic acid (DBA), a by-product of disinfection, develops in drinking water during chlorination or ozonation processes. Water intake is the main source of DBA exposure in humans, which is potentially neurotoxic. The present study investigated the neurotoxic effects of DBA by assessing the behavioral and biochemical characteristics of Sprague Dawley rats intragastrically treated with DBA at concentrations of 20, 50 and 125 mg kg−1 body weight for 28 consecutive days. The results indicated that animal weight gain and food consumption were not significantly affected by DBA. However, shuttle box tests showed increases in mistake frequency and reaction latency between the control and high-dose group. We found significant changes in hippocampal neurons by histomorphological observation. Additionally, biochemical analysis indicated enhanced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulting in disruption of cellular antioxidant defense systems including decreased mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and release of cytochrome c (cyt-c) from mitochondria into the cytosol, which can induce neuronal apoptosis. Furthermore, the increase of cyt-c in the cytosol enhanced caspase-3 and caspase-9 activity, which was confirmed by poly ADP-ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1) cleavage to its signature fragment of 85 kDa and decreased levels of protein kinase C-δ (PKC-δ) in the hippocampus. Meanwhile, DBA treatment caused differential modulation of apoptosis-associated proteins and mRNAs for phosphorylated apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1 (p-ASK-1), phosphorylated c-jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK), cyt-c, Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3 accompanied by DNA damage. Taken together, these data indicate that DBA may induce neurotoxicity via caspase-3-dependent apoptosis involving mitochondrial translocation of cyt-c in the rat hippocampus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...