Structure based in silico identification of potentially non-steroidal brassinosteroids mimics
Abstract
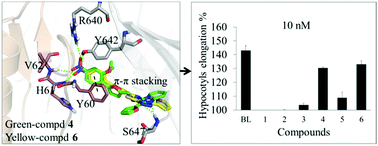
Brassinosteroids (BRs) are a class of plant steroid hormones that play indispensable roles in cell elongation, division and plant development. To date, the numerous synthesis of BRs analogs and structure–activity relationship investigations have clearly revealed the key substituent groups relevant to the steroidal activity of BRs. However, due to the limited chemical space studied, the efforts for alternative non-steroidal compounds have produced no remarkable results. To identify potentially non-steroidal BR mimics in this study, vital interacting pharmacophore features were extracted starting from several complex structures of BRs that bound with the receptor Brassinosteroid-Insentive 1 (BRI1) and co-receptor BRI1-associated kinase 1 (BAK1), which were characterized and merged into one comprehensive pharmacophore model. In silico screening of a commercial compound database was carried out by combing pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking and visual analysis. Finally, six non-steroidal molecules were identified and subjected to the in vivo radish hypocotyl elongation assay. As a positive control, the hypocotyls elongation for the naturally most active BR brassinolide (BL) is 152 ± 3% at 100 nM. Moreover, two candidates (4 and 6) show good BRs-like activity with the hypocotyls elongation of 143 ± 1% and 128 ± 3% at the same dose, respectively. Most remarkably, compounds 4 and 6, which have different structures, are predicted to share similar binding modes and proven to exhibit potential BRs-like activity. The two compounds obtained could be valuable leads for the development of BRs-like plant growth regulators.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...