EnhancerPred2.0: predicting enhancers and their strength based on position-specific trinucleotide propensity and electron–ion interaction potential feature selection†
Abstract
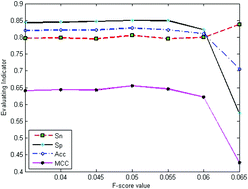
Enhancers are cis-acting elements that play major roles in upregulating eukaryotic gene expression by providing binding sites for transcription factors and their complexes. Because enhancers are highly cell/tissue specific, lack common motifs, and are far from the target gene, the systematic and precise identification of enhancer regions in DNA sequences is a big challenge. In this study, we developed an enhancer prediction method called EnhancerPred2.0 by combining position-specific trinucleotide propensity (PSTNP) information with the electron–ion interaction potential (EIIP) values for trinucleotides, to predict enhancers and their subgroups. To obtain the optimal combination of features, F-score values were used in a two-step wrapper-based feature selection method, which was applied in a high dimensional feature vector from PSTNP and EIIP. Finally, 126 optimized features from PSTNP combined with 32 optimized features from EIIP yielded the best performance for identifying enhancers and non-enhancers, with an overall accuracy (Acc) of 88.27% and a Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 0.77. Additionally, 198 features from PSTNP combined with 37 features from EIIP yielded the best performance for identifying strong and weak enhancers, with an overall Acc of 98.05% and a MCC of 0.96. Rigorous jackknife tests indicated that EnhancerPred2.0 was significantly better than the existing enhancer prediction methods in both overall accuracy and stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...