Feasibility study of particle detection and spectral diagnosis of plasma temperature through suspension introduction Ar-MPT-OES
Abstract
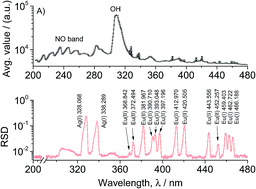
The Microwave Plasma Torch (MPT) is an excellent excitation source for on-line monitoring of environmental samples. However, the feasibility of particle detection and plasma diagnosis through particle introduction has not been reported yet. In this paper, Eu2O3/Ag and SiO2 suspensions were prepared, characterized and then introduced sequentially into the laboratory-made oxygen shielding argon flow MPT (OS-Ar-MPT) plasma for OES measurements with a time resolution of 6 ms. Signal spikes of Eu, Ag and Si lines from individual particles were observed, respectively, which demonstrates the feasibility of MPT-OES for particle detection. By using the line intensities from signal spikes and the measured sizes, the detection limits of the current instrument for Si, Ag and Eu in individual particles are estimated to be 1.8, 0.15 and 0.19 pg, respectively. The Eu(I) and Eu(II) line intensities extracted from the signal spikes were used to calculate the excitation temperature (Texc) of the OS-Ar-MPT plasma through the Boltzmann slope method. As a comparison study, the Texc was also calculated by using the traditional Fe(I) line Boltzmann slope method through solution introduction. The results show that Texc,Eu-I = 3293 K, Texc,Eu-II = 3414 K, and Texc,Fe-I = 4883 K. Meanwhile, the OH (0,0) band spectrum was simulated by varying the rotational temperature (Trot) by LIFBASE, and then compared with the measured spectrum when the Fe solution was nebulized. The best value of Trot lies between 3100 and 3400 K. Through this work, the capability of Ar-MPT-OES for particle detection is confirmed. Besides, the range of elements suitable for plasma diagnosis is widened and more diagnostic data of MPT plasma temperature are obtained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...