Homogenised 266 nm femtosecond laser ablation for isotopic and elemental microanalyses using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry†
Abstract
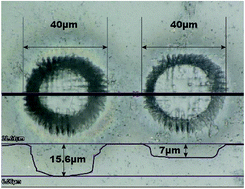
We report a beam-homogenizer with microlens arrays (lens array homogeniser: LAH) coupled with an ultraviolet (UV: 266 nm) femtosecond laser ablation (LA) system. The LAH generates a laser beam with a flat-top energy profile and a pulse width of ∼300 fs, originating from a frequency-tripled Ti-sapphire (TiS) laser source with a Gaussian energy profile and a pulse width of ∼170 fs. We examine the analytical performance of isotopic and elemental abundances using the 266LAH-FsLA system equipped with a multiple Faraday collector (MFC) and a sector field (SF) – inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICPMS). Stable and reasonably unfractionated samples of LA aerosols are collected from craters with diameter and depth in the range of 20–40 μm. Elemental fractionation between U and Pb in zircons is fairly small when a 20 μm LA crater is used. Quantitative analyses of 46 major and trace elements achieve a laboratory bias of less than 10% for most elements in a range from sub-ppm to several tens of wt% using the same crater size. The 266LAH-FsLA system performs a quantitative sampling in the spot mode. Flat ablation can also be used for quantitative sampling in LA-ICPMS imaging using the line scan mode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...