Conversion of HMF to methyl cyclopentenolone using Pd/Nb2O5 and Ca–Al catalysts via a two-step procedure†
Abstract
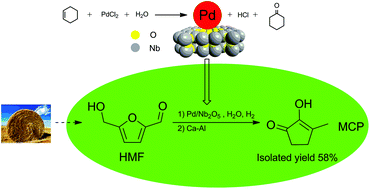
The catalytic conversion of HMF to 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one (MCP), which is a valuable edible essence that has traditionally been obtained from adipic acid, was achieved with an isolated yield of 58%. This procedure comprised two steps: the hydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) to 1-hydroxy-2,5-hexanedione (HHD) in water on Pd/Nb2O5 catalysts and then the isomerization of HHD to MCP in the presence of a base. The Nb2O5 supports, which were acidic, were characterized by FTIR, XRD and NH3-TPD. The supported Pd/Nb2O5 catalysts, in which Pd was highly dispersed, were synthesized employing cyclohexene as a reductant and were characterized by XRD, TEM, ICP-AES, XPS, EDX and CO pulse chemisorption. The high conversion of HMF was attributed to the high dispersion of Pd, and the acidity of the supports led to high selectivity for HHD. The conversion of HHD to MCP was an intramolecular aldol condensation reaction, and the protonic solvent favored this reaction. Ca–Al was proved to be an effective solid base for the conversion of HHD to MCP in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...