Co-Pyrolysis of torrefied biomass and methane over molybdenum modified bimetallic HZSM-5 catalyst for hydrocarbons production†
Abstract
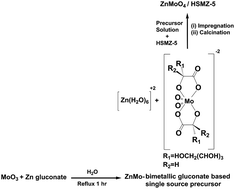
Catalytic pyrolysis of torrefied switchgrass under methane atmosphere was performed over molybdenum modified bimetallic catalysts. Compared with molybdenum-only catalysts (MoO3/HZSM-5 and Mo2C/HZSM-5), the bimetallic catalysts demonstrated a higher catalytic performance towards methane activation. Higher reaction temperatures favored formation of aromatic hydrocarbons under both helium and methane atmospheres. The maximum aromatic hydrocarbons yield of 39.31% was achieved during co-pyrolysis of raw switchgrass and methane over MoZn/HZSM-5 at 700 °C. Torrefaction prior to pyrolysis led to a decrease in the aromatic hydrocarbons yield. The yield of aromatic hydrocarbons from switchgrass torrefied at 270 °C was lower than that when torrefication was performed at 230 °C. The reduction of aromatic hydrocarbons from torrefied switchgrass is due to the loss of cellulose and the concomitant concentration of lignin during torrefaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...