Effect of nobiletin on the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in the synovial membrane of rats with arthritis induced by collagen
Abstract
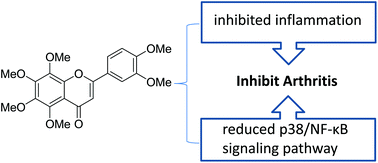
Nobiletin (5,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone) is a natural compound in the fruit peel of citrus fruit in the Rutaceae family. It is active in inhibiting inflammation, reducing plasma lipids and has anti-oxidative properties. In studying the effect of nobiletin on rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model on Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats was established by bovine type II collagen (BIIC), and the effect of nobiletin on RA was investigated using hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining, serum enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection and western blotting. The experimental results in animals revealed that the angiogenesis and inflammatory infiltration in synovial tissue, the serum pro-inflammatory cytokines of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels in BIIC immunized rats were significantly decreased after treatment with nobiletin. The protein expression levels of phosphorylated p38, p-p65 and the nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor alpha (IκBα) in the synovial membrane of CIA rats were down-regulated by nobiletin. These results demonstrated that nobiletin inhibited the development of RA by inhibiting the degree of angiogenesis and inflammatory infiltration by down-regulating the protein expression level of the p38/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway in the synovium of rats with CIA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...