Echinacoside ameliorates the memory impairment and cholinergic deficit induced by amyloid beta peptides via the inhibition of amyloid deposition and toxicology†
Abstract
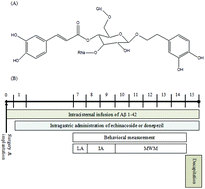
Echinacoside is a phenylethanoid glycoside and possesses neuroprotective activity in vitro and in vivo. This study investigates the role of the amyloid cascade and central neuronal function on the protective effects of echinacoside in amyloid β peptide 1-42 (Aβ 1-42)-treated SH-SY5Y cells and an Aβ 1-42-infused rat. Echinacoside inhibited Aβ 1-42 oligomerization in vitro and restored the cell viability that was reduced by Aβ 1-42 in SH-SY5Y cells. Intracisternal infusion with Aβ 1-42 by an osmotic pump caused cognitive deficits, an increase in amyloid deposition and acetylcholinesterase activities, and a decrease in the brain’s levels of acetylcholine and dopamine. Echinacoside reduced the cognitive deficits and amyloid deposition, and it reversed the cortical cholinergic dysfunction that was caused by Aβ 1-42 in rats. Echinacoside further reversed the memory impairment in the Morris water maze task caused by scopolamine in mice. Therefore, we suggest that echinacoside ameliorated cognitive dysfunction that was caused by Aβ 1-42 by blocking amyloid deposition via inhibiting amyloid oligomerization and reversing the cortical cholinergic neuronal function via decreasing amyloid neurotoxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...