Characterizing serum metabolic alterations of Alzheimer's disease and intervention of Shengmai-San by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry†
Abstract
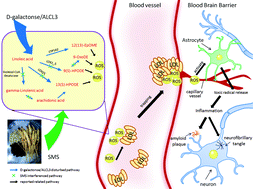
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic and multi-factor-induced neurodegenerative disorder. The development of a single-target treatment strategy for AD has not been successful. Shengmai-San (SMS), a traditional Chinese medicine containing multi-active components, has been reported to be effective for treating AD. However, the mechanism of SMS is still unclear, and as a multicomponent combination therapy, there is a lack of appropriate evaluation. Thereby, metabolomics was applied to investigate the multi-target intervention of SMS by monitoring the fold changes of metabolites in serum. An AD model was successfully replicated by treating rats with oral aluminum chloride (AlCl3) and an intraperitoneal injection of D-galactose (D-gal) for 105 days. The intervention group was treated with SMS during the whole modeling process. The results of classical experiments showed that SMS could alleviate Aβ1–40 deposition, protect neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and improve spatial learning and memory impairment compared with the model group. Based on these curative effects, a metabolomics study was implemented using the UPLC-Q/TOF-MS method. A heatmap of AD-associated metabolites (P < 0.05) was set up to target the most relevant metabolic network and to evaluate the comprehensive effects of SMS. Based on this AD-associated metabolic network, the total regulation-of-metabolites’ coverage rate of SMS was 51.35% and the gross metabolites’ recovery proportion was 72.32%. Lipid peroxidation was the main mechanism of SMS intervention in AD, including inhibition of the generation of linoleic acid hydroperoxides, such as 13-HPODE, 9-HPODE and 9-OxoODE.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...