Ethylcellulose oleogels for lipophilic bioactive delivery – effect of oleogelation on in vitro bioaccessibility and stability of beta-carotene
Abstract
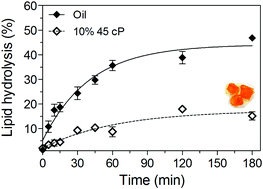
The in vitro lipolysis and β-carotene (BC) transfer from oil to aqueous phase of canola oil ethylcellulose (EC) oleogels were measured using a static monocompartmental model simulating oral, gastric, and duodenal digestive stages. The effects of EC oleogelation on gel in vitro digestibility were examined, using un-structured canola oil as a control. The physicochemical properties of oleogels containing BC were also measured. It was found that oleogels made with 10% 10 cP and 10% 20 cP did not differ significantly in their extent of lipolysis or BC transfer compared to canola oil; however 10% 45 cP and 15.5% 20 cP had a significantly lower extent of lipolysis and BC transfer compared to other formulations. The structure and mechanical strength of the oleogels were both determined to be factors affecting lipolysis and transfer. The presence of BC did not significantly affect the mechanical strength of the gels and EC oleogelation delayed BC degradation under accelerated storage conditions compared to a heated canola oil control. These findings could contribute to the development of new applications for EC oleogels, specifically for the effective delivery of lipophilic molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...