The protective effect of betulinic acid (BA) diabetic nephropathy on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
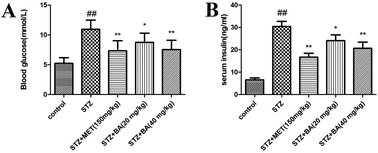
The present study was designed to investigate the protective effect of betulinic acid (BA) on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. The rats were intraperitoneally injected with STZ (35 mg kg−1). 7 days later, the animals were intragastrically administered with metformin (MET, 150 mg kg−1), BA (20 mg kg−1) or BA (40 mg kg−1) once daily for consecutive 30 days. The blood glucose, the contents of insulin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum were examined. The levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in kidney tissues were measured. Moreover, the histopathological alteration and the protein expressions of the signaling pathway were detected by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and western blotting, respectively. BA significantly decreased the levels of serum insulin, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and blood glucose. In addition, BA increased the activities of SOD, CAT and reduced the contents of MDA, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in kidney tissues. BA also ameliorated the histopathological condition. Furthermore, BA attenuated the phosphorylations of p-adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB), and an inhibitor of NF-κB (IκBα) and the expressions of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase (HO)-1. These findings demonstrated that BA exhibited a protective effect on diabetic nephropathy in STZ-induced rats possibly through the AMPK/NF-κB/Nrf2 pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...