Evaluation of clinical safety and beneficial effects of stachyose-enriched α-galacto-oligosaccharides on gut microbiota and bowel function in humans
Abstract
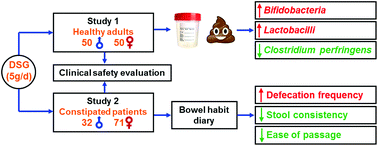
Deshipu stachyose granules (DSG) is a mixture of α-galacto-oligosaccharides derived from the dietary roots of Lycopus lucidus Turcz. Our previous study showed that DSG could improve the faecal microbial composition, and facilitate intestinal peristalsis and fecal excretion in mice. This study was designed to investigate the effect of DSG on gut microbiota and bowel function in humans. Two human intervention studies were conducted. In the first study, 100 healthy adults were treated without or with 5 g per day of DSG for 14 days. The microbiota composition in fecal samples was quantitatively analyzed before and after DSG supplementation. We found that DSG consumption significantly elevated the fecal bifidobacteria and lactobacilli levels, and also decreased the fecal Clostridium perfringens concentration. In the second study, 103 constipated patients were treated with 5 g per day of placebo or DSG for 30 days, and subsequently subjected to bowel function evaluation. As a result, dietary intake of DSG effectively improved the bowel function of constipated patients, as evidenced by the increased defecation frequency, softer stools and easier defecation. Moreover, clinical safety assessment showed that DSG at 5 g per day did not cause significant adverse effects in both healthy and constipated volunteers. In conclusion, DSG at 5 g d−1 beneficially modulated the gut microbiota in healthy adults and potently improved the bowel function of constipated patients without consequent adverse events. This study suggests that DSG holds promising potential for safe treatment of functional constipation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...