Membrane-based methods of virus concentration from water: a review of process parameters and their effects on virus recovery†
Abstract
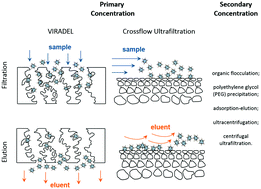
This review focuses on membrane-based methods of virus concentration from aqueous media. The discussion is centered on the two most commonly used sample concentration techniques: virus adsorption and elution (VIRADEL) and crossflow ultrafiltration (CFUF). We summarize all published VIRADEL and CFUF studies on the concentration of two human viral pathogens that are difficult to recover and quantify: noroviruses (17 reports total) and adenoviruses (15 reports total). We also include in the discussion all studies published since 2001 on the concentration of MS2, a bacteriophage commonly used in fate and transport studies as a surrogate of human viruses. The reported recoveries are analyzed in the context of key concentration process parameters including virus and membrane properties, initial virus content in the sample and details of the filtration protocol, as well as composition of the water and the eluent used to collect viruses adsorbed on the membrane surface. We conclude by identifying knowledge gaps and outlining a possible research agenda for improving the science and practice of virus separation for detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...