Highly efficient visible-light-induced photoactivity of Z-scheme Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation
Abstract
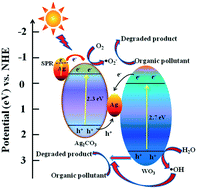
Novel and efficient Z-scheme Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 with excellent visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance was fabricated using a facile deposition and photochemical reduction process. Surface, morphological, and structural properties of the resulting materials were characterized using N2 sorption–desorption and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurements, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and UV-vis and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The photocatalytic performances of the Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 composites were evaluated by the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB), methyl orange (MO), ciprofloxacin (CIP), and tetracycline hydrochloride (TC) under visible light irradiation. The results demonstrate that the novel Z-scheme Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 composites exhibit higher photocatalytic activity than pure Ag2CO3 rods and WO3 nanoparticles. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 can be ascribed to the extended absorption in the visible light region caused by a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect, effective separation of photogenerated charges, and the formation of a Z-scheme system. In addition, the photocatalyst exhibits high stability and reusability. This work could offer a new insight into the design and fabrication of advanced materials with Z-scheme structures for photocatalytic applications for organic pollutants removal from wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...