The efficacy and environmental implications of engineered TiO2 nanoparticles in a commercial floor coating†
Abstract
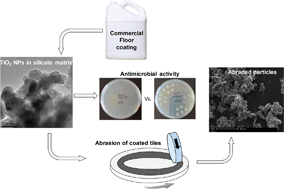
Engineered nanomaterials (ENM) have diverse applications in consumer products, but few studies weigh the improved product performance resulting from the inclusion of an ENM against the unintended consequences of released ENM. We developed and applied a framework to test a commercial floor coating that contains TiO2 nanoparticles in a silicate/siliconate matrix for both efficacy and exposure risk. Extracted TiO2 nanoparticles from the product were first characterized for particle size, morphology, mass concentration, and surface chemical composition prior to floor tile application. Porcelain tiles were coated with three TiO2 concentrations to understand the effect of TiO2 content on coating performance with respect to antimicrobial properties, abrasion resistance, and hydrophobicity. Coating porcelain tiles with the commercial product did not significantly enhance antimicrobial activity or scratch resistance compared to controls without TiO2 nanoparticles. Particles released during accelerated abrasion were collected and analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to inform exposure studies. During the abrasion test that simulated product use phase, TiO2 nanoparticles clusters were effectively removed from tile surfaces and embedded in a micron-sized silicate matrix. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in water by photocatalytic reactions using TiO2 from the coating were an order of magnitude lower than by a TiO2 nanoparticle standard. While the overall exposure risk to TiO2 nanoparticles released from floor coatings is low, we did not observe increased efficacy from adding TiO2 to the coating formulation. Product developers and policy makers may use the framework developed in this study to systematically assess the efficacy and product safety across a product's life cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...