Investigations into titanium dioxide nanoparticle and pesticide interactions in aqueous environments†
Abstract
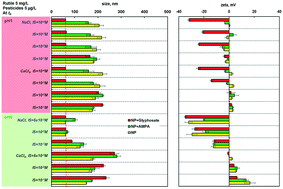
The influence of three pesticides (glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)) on the colloidal fate of TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs; anatase and rutile) has been investigated under aqueous conditions of variable chemical composition (Na+ or Ca2+), ionic strength (IS, 10−4–10−1 M), and pH (5 or 8). Sorption and degradation of these pesticides in the presence of the NPs were evaluated. In the absence of the pesticides, increasing IS, the presence of the divalent cation Ca2+ and a pH value close to the NP isoelectric point favored NP homoaggregation as expected. However, at low IS (≤10−2 M in NaCl; ≤10−3 M in CaCl2), in the presence of a few μg L−1 of glyphosate and rutile in the mg L−1 range, NP homoaggregation was prevented, despite the pH = 5 close to the NP isoelectric point (4.0–4.2). The phosphonate group of the pesticide drove glyphosate adsorption onto the NP, while the carboxylic group was responsible for the electrostatic stabilization of the NP. The stabilizing effect of glyphosate on NP aggregation however appears to be temporary. Furthermore, TiO2 NPs also adsorbed AMPA and promoted degradation of glyphosate to AMPA. These results highlight new evidence of NP–pesticide interactions and the differences in their fate and potential co-migration behavior in aquatic environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...