Synthesis and characterisation of new Bi(iii)-containing apatite-type oxide ion conductors: the influence of lone pairs
Abstract
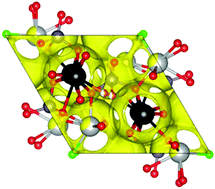
Lone-pair cations are known to enhance oxide ion conductivity in fluorite- and Aurivillius-type materials. Among the apatite-type phases, the opposite trend is found for the more widely studied silicate oxide ion conductors, which exhibit a dramatic decrease in conductivity on Bi(III) incorporation. In this work, the influence of lone-pair cations on the properties of apatite-type germanate oxide ion conductors has been investigated by preparing and characterising seven related compositions with varying Bi(III) content, by X-ray and neutron powder diffraction and impedance spectroscopy. All materials are very good oxide ion conductors (with conductivities of up to 1.29 × 10−2 S cm−1 at 775 °C). Increasing Bi(III) content leads to increases in conductivity by up to an order of magnitude, suggesting significant differences in the oxide-ion conduction mechanisms between lone-pair-containing apatite-type germanate and silicate solid electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...