Synthesis and methane cracking activity of a silicon nitride supported vanadium nitride nanoparticle composite†
Abstract
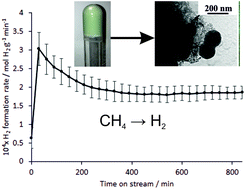
The co-ammonolysis of V(NMe2)4 and Si(NHMe)4 with ammonia in THF and in the presence of ammonium triflate ([NH4][CF3SO3]) leads to the formation of monolithic gels. Pyrolysing these gels produces mesoporous composite materials containing nanocrystalline VN and amorphous silicon imidonitride. Elemental mapping indicated a thorough distribution of VN with no evidence of large cluster segregation. Whilst not active for ammonia synthesis, the silicon nitride based materials were found to possess activity for the COx-free production of H2 from methane, which makes them candidates for applications in which the presence of low levels of CO in H2 feedstreams is detrimental.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Silicon Chemistry: Discoveries and Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...