Extension of catalyst lifetime by doping of Ce in Ni-loaded acid-washed Shengli lignite char for biomass catalytic gasification†
Abstract
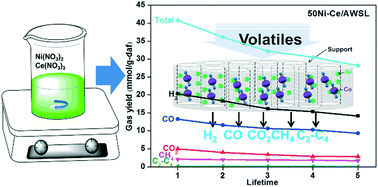
Cerium (Ce)-doped nickel (Ni)-based catalysts supported on modified lignite with HCl were prepared by a co-impregnation method with different Ni/Ce ratios (xNi-Ce/AWSL, where x is 1, 10, 20, 50, and 100, and AWSL is acid-washed Shengli lignite). The promotion effect of Ce with different Ni/Ce weight ratios on structural properties and activity under different atmospheres was investigated in detail. All catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and N2 physisorption apparatus. The performance of catalysts was evaluated in a well-designed reactor system for biomass catalytic gasification (BCG). The results indicated that the active component of Ni was dispersed uniformly, and that a high and stable gas yield was obtained over Ce-doped catalysts. Due to the formation of a Ni–Ce alloy, the Ce-doped catalyst with a Ni/Ce weight ratio of 50 : 1 showed the most stable gas yield (69.1%). After carrying out BCG five times, the lowest carbon deposition (weight increase of 1.7%) was obtained under an Ar atmosphere. Spent 50Ni–Ce/AWSL catalyst showed the least carbon deposition, and had the lowest Ni crystallite size (17.3 nm) and smallest average pore size (2.86 nm). The maximum catalytic activity and highest stability for BCG was observed for the catalyst with a Ni/Ce ratio of 50, which showed the best inhibition of carbon deposition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...