Organotin(iv) compounds with high catalytic activities and selectivities in the glycerolysis of triacylglycerides†
Abstract
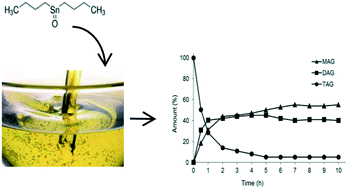
Sn(IV) complexes, i.e., di-n-butyltin dichloride (Bu2SnCl2), n-butyltin trichloride (BuSnCl3), di-n-butyltin dilaurate (Bu2SnLau2), n-butyl stannoic acid [BuSnO(OH)], and di-n-butyl-oxo-stannane (Bu2SnO), were tested as catalysts for the glycerolysis of triacylglycerides (TAGs) to produce monoacylglycerols (MAGs) and diacylglycerols (DAGs). Parameters such as the reaction time, temperature, catalyst amount and stirring velocity were evaluated. All complexes were active in converting TAGs to MAGs and DAGs. The reactivity order at 220 °C at a molar ratio of 1/6/0.01 (TAGs/GLY/CAT) was established as: Bu2SnO > Bu2SnLau2 ∼ BuSnO(OH) > Bu2SnCl2 > BuSnCl3. The results were discussed considering the different catalyst compatibilities with the reaction medium and the different mechanisms accepted for (trans)esterification catalysed by organotin(IV) compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...