Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of a novel, recyclable and stable photocatalytic nanoreactor for recognition and degradation of tetracycline†
Abstract
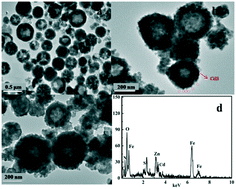
A unique Ppy@CdS/ZnFe2O4 nanoreactor is fabricated via the microwave-hydrothermal method and surface-imprinting technique, which effectively enhances the recyclability, stability, and selectivity for recognition and degradation of tetracycline under visible-light irradiation. The as-prepared functional nanoreactor enables photocatalytic reactions with little loss of activity during the recycling process. In addition, the capture experiments and ESR exploration show that h+ and ˙OH play the major roles in this photocatalytic reaction. Therefore, this study not only puts forward a novel design concept that develops the potential application value of CdS, but also provides a new approach for inhibiting its secondary pollution. Moreover, this nanoreactor has huge potential for the continuous and selective decomposition of specific pollutant molecules according to practical requirements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...