In situ encapsulation of platinum clusters within H-ZSM-5 zeolite for highly stable benzene methylation catalysis†
Abstract
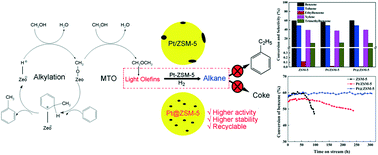
The catalytic conversion of benzene and methanol to alkyl aromatic products is a promising way of converting nonpetroleum sources to fine chemicals. Ethylbenzene is the major by-product, which is still difficult to suppress. Besides, coke deposition on ZSM-5 catalysts is of serious concern on account of its impact on the catalyst deactivation and consequent loss in the production yield. In this study, Pt@ZSM-5 catalysts were synthesized using in situ hydrothermal synthesis techniques. The resultant catalysts exhibit a higher activity (60.1%) in comparison with impregnated Pt/ZSM-5 catalysts (56.3%), which is ascribed to the preservation of the pore volume and surface area in the resulting material. Notably, thanks to the high dispersion of Pt particles within the ZSM-5 nanocrystals, the Pt@ZSM-5 catalysts show superior anti-coking performance without deactivation after 300 h on stream, along with a high suppression ability towards the formation of ethylbenzene (<0.01%). Meanwhile, the confinement within the ZSM-5 crystals protects the Pt clusters from sintering and coalescence during thermal regeneration treatments. Such novel Pt@ZSM-5 catalysts exhibit excellent activity, remarkable stability and outstanding recyclability, thus providing an opportunity for benzene alkylation with methanol towards industrial production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...