Interfacial effects of MnOx-loaded TiO2 with exposed {001} facets and its catalytic activity for the photoreduction of CO2†
Abstract
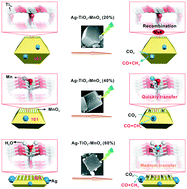
Herein, anatase TiO2 with different percentages of exposed {001} and {101} facets was prepared, and subsequently, Ag and MnOx were co-loaded on these TiO2 facets through a classical photodeposition method; the loaded TiO2 samples were labeled as Ag–TiO2–MnOx (N%), where N% denotes the percentage of the exposed {001} facets. The as-prepared samples were analyzed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), and the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 was carried out. The results showed that Ag–TiO2–MnOx (40%) exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity among the other dual-loaded samples and pure TiO2. The XPS spectra demonstrated that Ti–O–Mn and Ti–O–H bonds were formed at the interfaces of the cocatalyst-TiO2. The PL and VB spectra revealed that the chemical bond (Ti–O–Mn) at the Ag–TiO2–MnOx (40%) interface greatly increased the hole mobility rate and the photoinduced carrier separation efficiency that resulted in higher catalytic activity for the photoreduction of CO2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...