Tripodal amine ligands for accelerating Cu-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition: efficiency and stability against oxidation and dissociation†
Abstract
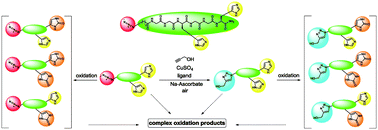
Ancillary ligands, especially the tripodal ligands such as tris(triazolylmethyl)amines, have been widely used to accelerate Cu-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC, a “click” reaction). However, the relationship between the activity of these Cu(I) complexes and their stability against air oxidation and ligand dissociation/exchange was seldom studied, which is critical for the applications of CuAAC in many biological systems. In this work, we synthesized twenty-one Cu(I) tripodal ligands varying in chelate arm length (five to seven atoms), donor groups (triazolyl, pyridyl and phenyl), and steric hindrance. The effects of these variables on the CuAAC reaction, air oxidation, and ligand dissociation were evaluated. Reducing the chelate arm length to five atoms, decreasing steric hindrance, or using a relatively weakly binding ligand can significantly increase the CuAAC reactivity of the Cu(I) complexes, but the concomitant higher degree of oxidation cannot be avoided, which leads to rapid degradation of a histidine-containing peptide as a model of proteins. The oxidation of the peptide can be reduced by attaching oligo(ethylene glycol) chains to the ligands as sacrificial reagents. Using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), we directly observed the tri- and di-copper(I)-acetylide complexes in the CuAAC reaction in the [5,5,5] ligand system and a small amount of di-Cu(I)-acetylide in the [5,5,6] ligand system. Only the mono-Cu(I) ligand adducts were observed in the [6,6,6] and [5,6,6] ligand systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...