On the Mn promoted synthesis of higher alcohols over Cu derived ternary catalysts†
Abstract
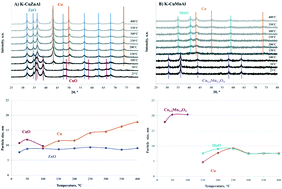
This work provides insight into the promotional effect of Mn on the synthesis of higher alcohols over Cu-based ternary catalysts through XPS and in situ DRIFTS and powder XRD. These revealed that the surface of K-CuZnAl, an active catalyst for CO hydrogenation to methanol, possesses Cu+ sites able to adsorb CO associatively and Cu0 sites for H2 dissociation. Here we show that exchanging Zn with Mn induces a strong interaction between Cu and Mn that decreases the overall copper surface area and increases the Cu+/Cu0 ratio. In situ DRIFTS showed that electronic modification of Cu+ sites by proximate Mn favors dissociative CO chemisorption, resulting in the formation of C and O adspecies that are precursors to higher alcohol formation. The decrease in metallic copper limits available sites for H2 dissociation, and hence retards the hydrogenation of oxygen-containing intermediates, thereby further promoting carbon-chain growth. Mn also increases the dispersion of the K promoter over the catalyst surface, providing abundant basic sites for aldol-type condensation reactions to branched oxygenates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...