Layer-dependent catalysis of MoS2/graphene nanoribbon composites for efficient hydrodesulfurization†
Abstract
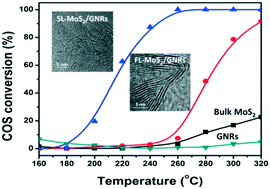
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) derived from the unzipping of carbon nanotubes are used as a catalyst carrier for MoS2 with different layers via a facile solution route. Efficient hydrodesulfurization (HDS) of carbonyl sulfide (COS) has been achieved over the MoS2/GNR composites. It is revealed that single layer MoS2 anchored on GNRs (SL-MoS2/GNRs) is successfully fabricated by the assistance of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The catalytic activities of the SL-MoS2/GNRs, few-layer MoS2 supported on GNRs (FL-MoS2/GNRs) and pure MoS2 with a multi-layer structure (ML-MoS2) are investigated, and the layer-dependent catalytic activity of MoS2 has been demonstrated in the hydrogenation of COS. The order of the catalytic performance for the three catalysts is SL-MoS2/GNRs > FL-MoS2/GNRs > ML-MoS2, especially within a low temperature range (180–280 °C) of the HDS reaction. The superior catalytic activity of SL-MoS2/GNRs can be ascribed to the high density of the active sites in single-layer MoS2. Due to the edge effect of GNRs, single layer MoS2 supported on GNRs is thinner and shorter than MoS2 anchored on graphene nanosheets (GS). The synergy between single layer MoS2 and GNRs may be mainly responsible for the better catalytic performance of SL-MoS2/GNRs. This work offers a feasible strategy for the synthesis of single-layer MoS2 supported on GNRs for efficient HDS application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...