Electronic and bite angle effects in catalytic C–O bond cleavage of a lignin model compound using ruthenium Xantphos complexes†
Abstract
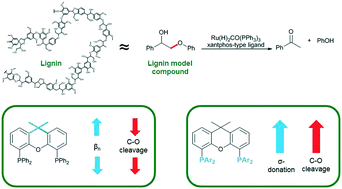
Bite angle and electronic effects on the ruthenium–diphosphine catalysed ether bond cleavage of the lignin β-O-4 model compound 2-phenoxy-1-phenylethanol were tested. Enhanced conversion of the substrate was observed with increasing σ-donor capacity of the ligands. Kinetic and thermodynamic data suggest oxidative addition of the dehydrogenated model compound to the diphosphine Ru(0) complex to be rate-limiting.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...