Electroanalytical study of dopamine oxidation on carbon electrodes: from the macro- to the micro-scale
Abstract
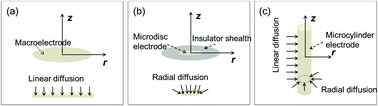
The oxidation of dopamine in strongly acidic (pH = 0) solution is investigated using microdisc, microcylinder and macro-electrodes together with a range of voltage scan rates. Kinetic and mechanistic analysis over the full range of mass transport conditions show a behaviour consistent with an ECE process with a fast chemical step and in which the second electron transfer is thermodynamically more favourable than the first step. Accordingly the reaction effectively behaves as an EE process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...