Fluorescence quenching of the N-methylquinolinium cation by pairs of water or alcohol molecules†
Abstract
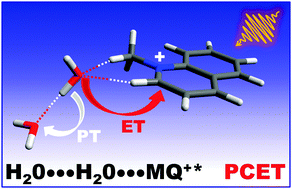
N-Methylquinolinium cation (MQ+) in its first-excited singlet state is a strong oxidant commonly used as a photosensitizer, whose fluorescence is therefore quenched by electron donors. Interestingly, the fluorescence of MQ+ is also quenched by hydroxy compounds such as water and alcohols, more difficult to oxidize. We investigated the quenching mechanism of MQ+ fluorescence by small amounts of water and alcohols in acetonitrile solution. The fluorescence intensities and lifetimes exhibited a nonlinear dependence on the quencher concentration. We found evidence that emissive exciplexes MQ+*-ROH are formed between the excited quinolinium and the hydroxy compounds. An accurate quantitative description of the results was obtained with a model in which the exciplex reacts with a second molecule of the hydroxy compound, which quenches the fluorescence. The rate constant of this process increased as the quencher ionization energy decreased. We showed also that a low basicity of the hydroxy compound inhibits the quenching process. These results are consistent with the existence of a concerted photoinduced proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) involving an intermediate complex of the excited quinolinium with a H-bonded molecular pair of the hydroxy compounds. In these pairs, a water or an alcohol molecule is able to donate an electron to the photoexcited quinolinium cation and a proton to the second H-bonded hydroxy molecule, showing an enhanced reducing power in comparison with the isolated molecule. The structure of the intermediate complex was investigated using high-level quantum mechanical calculations. At high water concentrations in acetonitrile/water mixtures, the quenching process is slowed down, indicating that higher water aggregates are less effective for a PCET process. The results obtained may be relevant to the study of water oxidation and electron transfer in biological systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...