Reversibly photo-switchable wettability of stearic acid monolayer modified bismuth-based micro-/nanomaterials†
Abstract
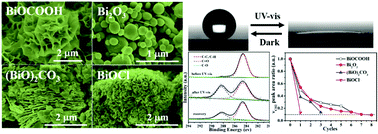
In this work, we demonstrated a general approach to realize superhydrophobic–superhydrophilic reversible transition over hydrophilic bismuth-related micro-/nanomaterials. Different superhydrophobic bismuth-based micro-/nanomaterials, including BiOCOOH, Bi2O3, (BiO)2CO3 and BiOCl, were obtained by modification with stearic acid, regardless of their morphologies. The reversible wettability of the bismuth-related materials upon alternative UV-vis irradiation and dark storage were investigated via cyclic experiments. The results indicated that the reversible wetting behavior was highly related with the photocatalytic activities of the bismuth-based materials. High photocatalytic activity resulted in less reversible cycles between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity due to the photodegradation of stearic acid. Moreover, with the increase of cycle number, the required minimal time for photo-induced superhydrophilicity decreased and the minimal time for the recovery of superhydrophobicity under dark storage increased. Based on peak deconvolution analysis of XPS and FTIR spectra, a comprehensive understanding of reversible wettability of the bismuth-related micro-/nanomaterials was proposed. This work provides a new strategy to fabricate superhydrophobic–superhydrophilic switchable surfaces for most hydrophilic inorganic materials with different morphologies and photocatalytic activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...