High cross-plane thermoelectric performance of metallo-porphyrin molecular junctions†
Abstract
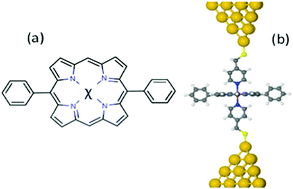
We investigated the thermoelectric properties of flat-stacked 5,15-diphenylporphyrins containing divalent metal ions Ni, Co, Cu or Zn, which are strongly coordinated with the nitrogens of pyridyl coated gold electrodes. Changing metal atom has little effect on the thermal conductance due to the phonons. The room-temperature Seebeck coefficients of these junctions are rather high, ranging from 90 μV K−1 for Cu, Ni and Zn-porphyrins to −16 μV K−1 for Co-porphyrin. These values could be further increased by lowering molecular energy levels relative to the DFT-predicted Fermi energy. In contrast, the phonon contribution to the thermal conductance of these junctions is rather insensitive to the choice of metal atom. The thermopower, thermal conductance and electrical conductance combined to yield the room-temperature values for the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT ranging from 1.6 for Cu porphyrin to ∼0.02 for Ni-porphyrin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...