The effect of Y3+ substitution on the structural, optical band-gap, and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles
Abstract
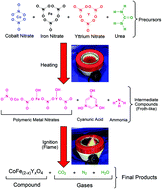
In this study we investigated the structural, optical band-gap, and magnetic properties of CoYxFe2−xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.04) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized using a combustion reaction method without the need for subsequent heat treatment or the calcing process. The particle size measured from X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and transmission electron microscope (TEM) images confirms the nanostructural character in the range of 16–36 nm. The optical band-gap (Eg) values increase with the Y3+ ion (x) concentration being 3.30 and 3.58 eV for x = 0 and x = 0.04, respectively. The presence of yttrium in the cobalt ferrite (Y-doped cobalt ferrite) structure affects the magnetic properties. For instance, the saturation magnetization, Ms and remanent magnetization, Mr, decrease from 69 emu g−1 to 33 and 28 to 12 emu g−1 for x = 0 and x = 0.04, respectively. On the other hand the coercivity, Hc, increases from 1100 to 1900 Oe for x = 0 and x = 0.04 at room temperature. Also we found that Ms, Mr, and Hc decreased with increasing temperature up to 773 K. The cubic magnetocrystalline constant, K1, determined by using the “law of approach” (LA) to saturation decreases with Y3+ ion concentration and temperature. K1 values for x = 0 (x = 0.04) were 3.3 × 106 erg cm−3 (2.0 × 106 erg cm−3) and 0.4 × 106 erg cm−3 (0.3 × 106 erg cm−3) at 300 K and 773 K, respectively. The results were discussed in terms of inter-particle interactions induced by thermal fluctuations, and Co2+ ion distribution over tetrahedral A-sites and octahedral B-sites of the spinel structure due to Y3+ ion substitution.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...