Microscopic nucleation and propagation rates of an alanine-based α-helix†
Abstract
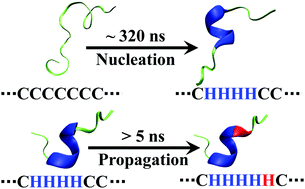
An infrared temperature-jump (T-jump) study by Huang et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2002, 99, 2788–2793) showed that the conformational relaxation kinetics of an alanine-based α-helical peptide depend not only on the final temperature (Tf) but also on the initial temperature (Ti) when Tf is fixed. Their finding indicates that the folding free energy landscape of this peptide is non-two-state like, allowing for the population of conformational ensembles with different helical lengths and relaxation times in the temperature range of the experiment. Because α-helix folding involves two fundamental events, nucleation and propagation, the results of Huang et al. thus present a unique opportunity to determine their rate constants – a long-sought goal in the study of the helix–coil transition dynamics. Herein, we capitalize on this notion and develop a coarse-grained kinetic model to globally fit the thermal unfolding curve and T-jump kinetic traces of this peptide. Using this strategy, we are able to explicitly determine the microscopic rate constants of the kinetic steps encountered in the nucleation and propagation processes. Our results reveal that the time taken to form one α-helical turn (i.e., an α-helical segment with one helical hydrogen bond) is about 315 ns, whereas the time taken to elongate this nucleus by one residue (or backbone unit) is 5.9 ns, depending on the position of the residue.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...