Dispersion interactions in silicon allotropes†
Abstract
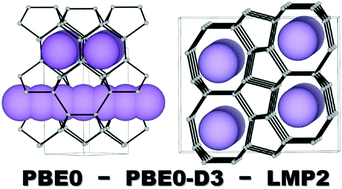
van der Waals interactions are known to play a key role in the formation of weakly bound solids, such as molecular or layered crystals. Here we show that the correct quantum-chemical description of van der Waals dispersion is also essential for a correct description of the relative stability between purely covalently-bound solids like silicon allotropes. To this end, we apply periodic local MP2 and DFT with Grimme's empirical –D3 correction to 11 experimentally determined or yet hypothetical crystalline silicon structures, including the most recently discovered silicon allotropes. Both methods provide similar energy ordering of the polymorphs, which, at the same time, noticeably deviate from the order predicted by standard DFT without an appropriate description of the van der Waals dispersion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...