Effect of adsorption kinetics on dissociation of DNA-nucleobases on gold nanoparticles under pulsed laser illumination†
Abstract
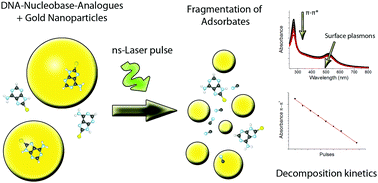
Photothermal therapy is a novel approach to destroy cancer cells by an increase of temperature due to laser illumination of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) that are incorporated into the cells. Here, we study the decomposition of DNA nucleobases via irradiation of gold nanoparticles with ns-laser pulses. The kinetics of the adsorption and decomposition process is described by a theoretical model based on the Langmuir assumptions and correlated with experimentally determined reaction rates revealing a strong influence of the nucleobase specific adsorption. Beside the four nucleobases, their brominated analogs, which are potential radiosensitizers in cancer therapy, are also investigated and show a significant modification of the decomposition rates. The fastest decomposition rates are observed for adenine, 8-bromoadenine, 8-bromoguanine and 5-bromocytosine. These results are in good agreement with the relative adsorption rates that are determined from the aggregation kinetics of the GNPs taking the effect of an inhomogeneous surface into account. For adenine and its brominated analog, the decomposition products are further analyzed by surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) indicating a strong fragmentation of the molecules into their smallest subunits.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bunsentagung 2017: Physical Chemistry for Life Sciences


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...