Free-standing reduced graphene oxide/MnO2–reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite flexible membrane as an anode for improving lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
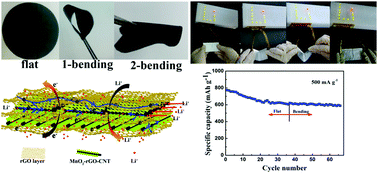
To solve the barriers of poor rate capability and inferior cycling stability for the MnO2 anode in lithium ion batteries, we present a highly flexible membrane anode employing two-dimensional (2D) reduced graphene oxide sheets (rGO) and a three-dimensional (3D) MnO2–reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite (MGC) by a vacuum filtration and thermal annealing approach. All the components in the 2D/3D thin film anode have a synergistic effect on the improved performance. The initial discharge specific capacity of the electrode with the MnO2 content of 56 wt% was 1656.8 mA h g−1 and remains 1172.5 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a density of 100 mA g−1. On enhancing the density to 200 mA g−1, the membrane-electrode still exhibits a large reversible discharging capacity of ∼948.9 mA h g−1 after 300 cycles. Moreover, the flexible Li-ion battery with a large area also shows excellent electrochemical performance in different bending positions, which provides the potential for wearable energy storage devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...