Selective adsorption behaviour of carbon dioxide in OH-functionalized metal–organic framework materials†
Abstract
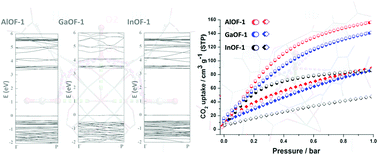
The theoretically optimal adsorption locations in hydroxyl (OH)-decorated metal–organic frameworks show that the captured carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules interact with the cis-μ2-OH groups in an end-on mode, which shows a moderate to weak hydrogen bond. The experimental isotherms and ideal adsorption solution theory (IAST) calculations show the high selectivity of CO2 for nitrogen at 273, 283 and 295 K and 1.0 bar for three types of OH-appended isostructures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Crystalline Materials for Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...