Morphological evolution of hierarchical Bi2Se3/BiOBr nanostructures and enhanced activity for p-nitrophenol reduction by NaBH4†
Abstract
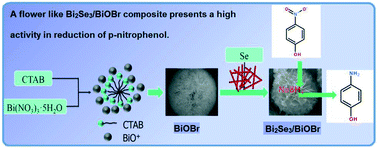
An emerging Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite with a flower-like microsphere structure has been synthesized by a solvothermal method using CTAB as a template agent. It is found that the obtained Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite showed a good catalytic performance for the hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol. The catalytic times of the conversion of up to 90% for the Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite, Bi2Se3 and BiOBr are about 5.0, 12.5 and 15.0 min, respectively. The enhanced catalytic activity of the Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite results from a synergistic effect of Bi2Se3 and BiOBr, probably owing to the unique structure, and the combination promotes the transfer of electrons. A self-assembling growth mechanism of the Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite is proposed by observing the morphology and composition of the products at different times. It is found that BiOBr microspheres first formed, then BiOBr microspheres gradually reacted with selenium powder to grow the Bi2Se3/BiOBr composite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...