Effect of lithium doping and precursors on the microstructural, surface electronic and luminescence properties of single crystalline microtubular tin oxide structures†
Abstract
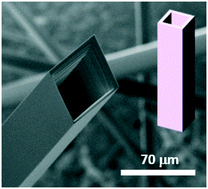
Li doped SnO2 microtubes were obtained by thermal evaporation using two different starting materials as precursors: Li doped SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a soft chemistry method or a mixture of commercial SnO2 and Li2CO3 powders. In both cases the controlled lithium content was in the range from 10 to 30 cationic %. The microstructures are grown following a vapor–solid mechanism assisted by dislocations. The density of the obtained structures was slightly lower for the nanoparticle-based samples, although the treatments last for longer times in comparison to that of the commercial mixture-based samples. A study of the surface electronic properties and the luminescence emission of the different microtubes reveals a variable defect distribution in the samples depending on the precursor used. Oxygen vacancies and/or tin interstitials are generated to compensate for the charge imbalance due to the lithium incorporation in tin lattice sites together with the reduction of neighboring tin atoms. The microstructural characterization of the samples has been carried out by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and electron backscattered diffraction. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and cathodoluminescence measurements allow comparison of pathways which favor the incorporation of the dopant into the structure and the interaction of lithium with native defects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...