3D hierarchical macro/mesoporous TiO2 with nanoporous or nanotubular structures and their core/shell composites achieved by anodization
Abstract
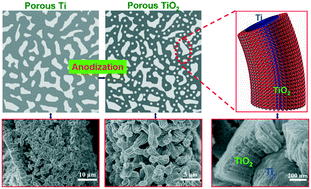
TiO2 is one of the most extensively investigated materials owing to its unique properties and several promising applications. The properties of TiO2 are highly dependent on its microstructure and feature size. Herein, we report a strategy for the synthesis of hierarchical porous TiO2 with two distinguishable scales of ligament sizes, which consists of both macro-pores and meso-pores. A metallic melt dealloying process with CuTi alloy was followed to form a porous Ti precursor. Subsequently, this precursor was used as a substrate for anodization to form TiO2. By controlling the anodization potential, time and initial porous Ti ligament size, nanotubular nanotubes or nanoporous TiO2 were distributed uniformly on the ligaments of porous Ti. Both the sizes of the macropore (400 nm to 2 μm) and mesopore (10 to 30 nm) can be tuned. A core–shell structured TiO2/Ti composite with a nanoporous or nanotubular structure in the shell and un-anodized porous Ti in the core can be achieved by partial anodization. The hierarchical structure with high surface area is essential for mass transport (large pore) and functionality (small pore), which makes it a potential candidate for various applications such as in sensors and catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...