Effect of functionalities on the crystal structures of new zinc(ii) dithiocarbamates: a combined anti-leishmanial and thermal decomposition study†
Abstract
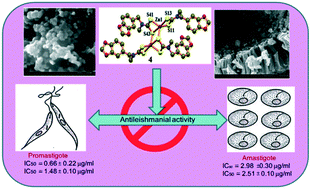
New homoleptic zinc(II) dithiocarbamates, [Zn(L)2] (L = N-ferrocenyl-N-methyl dithiocarbamate (L1) 1, (N-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl)-N-furfuryl) dithiocarbamate (L2) 2, N-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl)-(N-benzyl) dithiocarbamate (L3) 3, N-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl)-(N-methyl) dithiocarbamate (L4) 4, N-ethylmorpholine-(N-4-methoxyphenylmethyl) dithiocarbamate (L5) 5 and N-(benzo[d][1,4]dioxol-6-ylmethyl)-(N-benzylmethyl) dithiocarbamate (L6) 6, have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analyses and spectroscopy (IR, UV-vis, 1H and 13C{1H} NMR). X-ray crystallography revealed different dimeric structures for (1 and 2) and (3, 4, and 5) adopting distorted tetrahedral and TBP/SP coordination geometries, respectively, in which the dithiocarbamate ligands are bonded to the metal centers both in terminal S,S-chelating and μ2,κ2S,S-bridging and μ2,κ2-S,S-chelating–bridging arrangements. 6 is a mononuclear complex showing a distorted tetrahedral geometry. The supramolecular frameworks in these complexes have been sustained by C–H⋯S, C–H⋯O, C–H⋯π, π⋯π, C–H⋯π (ZnCS2, chelate) and H⋯H interactions. The anti-leishmanial activities of the complexes have been screened; 4 and 6 showed potential anti-promastigote and anti-amastigote activities with IC50 values of 0.66 ± 0.22, 1.48 ± 0.10 μg mL−1 and IC50 2.98 ± 0.30, 2.51 ± 0.10 μg mL−1, respectively. Cytotoxicity assays on both complexes showed toxicity on promastigotes but lower toxicity against the RAW 264.7 cell line at different concentrations. All the complexes show luminescence characteristics in CH2Cl2 solution at room temperature arising from the metal perturbed intra-ligand charge transfer (ILCT) states. Their TG analyses show single step decomposition with formation of binary ZnS and ternary FeZn2S3 materials which have been examined by PXRD, SEM and EDAX.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...