Improved microwave absorption performance of modified SiC in the 2–18 GHz frequency range
Abstract
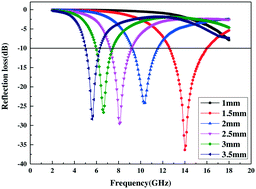
Aiming to improve the microwave absorption performance of SiC, various methods including doping and changing the shape were adopted. In view of doping, B-doped silicon carbide (B–SiC) with a B content of 3 mass% was prepared via a simple carbothermal reduction method. By using different raw materials, SiC both in nanowire and powder forms was obtained. The microwave absorption performance was investigated. The results show that B–SiC nanowires exhibit a far more improved microwave absorption ability in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz compared with SiC nanowires. The effective absorption bandwidth of the reflection loss below −10 dB is 3.52 GHz, and the maximum reflection loss of −37.94 dB at 14 GHz with a thickness of 1.5 mm indicates that B–SiC nanowires could be used as an effective microwave absorbing material. The combination of the enhanced electrical conductivity caused by B doping and the network formed from nanowires contributes to the enhanced microwave absorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...