Physiological pH-dependent gelation for 3D printing based on the phase separation of gelatin and oxidized dextran†
Abstract
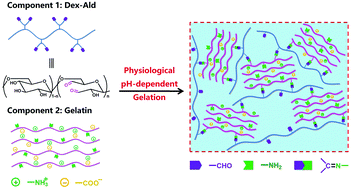
An extrudable hydrogel with a tunable gelation time under physiological pH ranges based on the phase separation of gelatin and oxidized dextran was demonstrated. We envision that the easy handing properties of this hydrogel combined with thermosensitive physical gelation and postponed chemical reinforcing will provide a platform for 3D bioprinting applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...