Gd3+-Doped MoSe2 nanosheets used as a theranostic agent for bimodal imaging and highly efficient photothermal cancer therapy†
Abstract
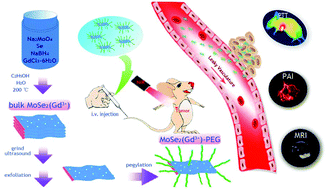
Recently, two dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) being used as nanomedicine have aroused great interest because of their unique photothermal properties. A simple liquid-phase method was used to prepare gadolinium (Gd3+)-doped molybdenum selenide (MoSe2) nanosheets, and then using poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) modification on the surface, MoSe2(Gd3+)-PEG nanosheets were obtained which had high stability in physiological solutions and showed no obvious toxicity in vivo. It revealed that Gd3+ used as a paramagnetic material for MoSe2(Gd3+)-PEG provided a strong contrast effect in magnetic resonance imaging, furthermore, the MoSe2 showed strong absorption in the near infrared region, and therefore, MoSe2(Gd3+)-PEG could be used as contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging (PAI). In in vitro experiments, it was found that MoSe2(Gd3+)-PEG could effectively increase the temperature to help kill cancer cells under laser irradiation. In vivo experiments showed that there was an enhanced permeation and retention effect in the tumor after intravenous injection measured using magnetic resonance/photoacoustic (MR/PA) bimodal imaging. After photothermal therapy, a significant suppression effect was achieved for tumors in mice by injection of these nanosheets with laser irradiation. This work emphasized that the simple doped TMDC nanomaterials when combined with treatment and imaging functions achieve a cancer therapy, which will provide a good opportunity for future diagnosis and treatment of cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...