MicroRNA detection by an amplification-free biosensor based on controllable solid-state electrochemiluminescence quenched by charge transfer
Abstract
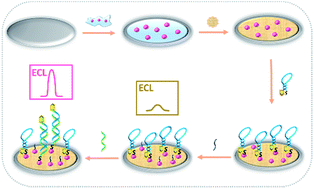
Effective and sensitive microRNA detection is a great challenge. Most microRNA assays use an amplification strategy to obtain high sensitivity, which makes them complicated. Herein, we present a simple and amplification-free solid-state electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor for the detection of miRNA based on high effective quenching by ferrocene and using N-butyldiethanolamine (BDEA) as a more effective co-reactant. Initially, the mixture of Nafion and Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) was cast onto the glassy carbon electrode (GCE) to form a Nafion–AuNPs film. The resulting electrode was then immersed into a solution of Ru(bpy)32+, where the solid-state Nafion–AuNPs/Ru(bpy)32+ could be obtained via electrostatic adsorption. The DNA molecular beacon, which was modified with thiol at one distal and the other was labeled with ferrocene (i.e., Fc-MB), was covalently attached to AuNPs on the ECL film through a Au–S bond. Afterwards, the remaining active sites of nonspecific adsorption were blocked with 6-mercapto-1-hexanol (MCH). When the target miRNA was present, it hybridized with the complementary part in the loop of Fc-MB and formed a double-stranded structure. This conformational change led the quencher away from the electrode, resulting in a remarkable increase in ECL intensity. Under the optimum condition, the ECL signal had a linear relationship with miRNA concentration ranging from 0.01 pM to 1 × 103 pM, with a limit of detection of 10 fM. Moreover, our biosensor showed remarkable specificity, outstanding reproducibility, good stability and excellent performance in real sample investigation with no amplification. Therefore, this developed strategy has great potential in early miRNA-related cancer diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...