Glutathione-S-transferase-catalyzed reaction of glutathione for electrochemical biosensing of temephos, fenobucarb and dimethoate†
Abstract
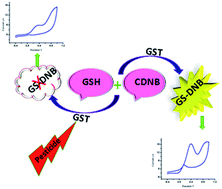
This study describes a sensitive bio-electrochemical detection method for extensively used toxic organothiophosphate pesticides temephos and dimethoate, and organocarbamate fenobucarb, by employing a simple mediatorless cyclic voltammetric technique. The sensing scheme is based on the inhibition of the catalytic activity of glutathione-s-transferase using these pesticides during the course of the conjugation reaction between reduced glutathione and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, resulting in a reduction in the oxidation peak current of the activated glutathione oxidation. The types of inhibition of these three pesticides were studied. Fenobucarb showed competitive inhibition with a Ki value of 10.30 mM, temephos showed non-competitive inhibition with a Ki value of 54.82 mM and dimethoate exhibited a mixed type of inhibition. Calibration curves for all the three pesticides were obtained with detection limits down to 2, 4 and 5 ppb for fenobucarb, temephos, and dimethoate, respectively. The method was validated with a spiked tomato sample using the standard solid-phase extraction clean-up method. The method is a promising new tool for analysis of water-insoluble organophosphate and organocarbamate pesticides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...