An ultra-sensitive 2D electrochemical sensor based on a PtNPs@graphene/Nafion nanocomposite for determination of α1-AR antagonist silodosin in human plasma†
Abstract
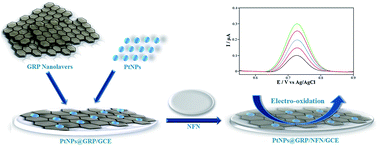
This paper reports a platinum nanoparticles/graphene/Nafion nanocomposite (PtNPs@GRP/NFN) as a novel and highly sensitive two-dimensional (2D) sensing nanoplatform for the electrochemical determination of silodosin (SLN). The electrochemical behavior of SLN was investigated at the proposed sensor (PtNPs@GRP/NFN/GCE) using adsorptive stripping differential pulse voltammetry (AdsDPV). The PtNPs@GRP nanocomposite was synthesized effectively from graphene oxide (GO) and Pt salt by a single-step chemical reduction method. The morphology and structure of the PtNPs@GRP nanocomposite were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Electrochemical characterization was also performed by cyclic voltammetry (CV) at the PtNPs@GRP/NFN/GCE. The sensor exhibited extraordinary electrochemical activity towards the SLN at nanomolar levels. Under optimal conditions, a sufficiently linear calibration curve in the range of 1.8–290.0 nM with an extremely low detection limit of 0.55 nM (S/N = 3) was obtained at the PtNPs@GRP/NFN/GCE. This sensor was successfully applied to determine the content of SLN in human plasma with satisfactory results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...