Nitrilotriacetate-stabilized gold nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the colorimetric detection of Cr(iii)/Cr(vi) and the mechanistic aspects†
Abstract
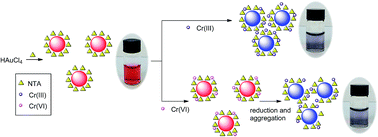
Nitrilotriacetate (NTA) has been reported to behave as both a reductant and a stabilizer for gold nanoparticle (AuNP) preparation in a one-pot synthesis and colorimetric assay. The goal of this study was to avoid the negative influence of citrate residues in the detection of chromium ions because citrate always remains in the modification of AuNPs via common ligand-exchange methods. This colorimetric assay was shown to be highly efficient and selective for the detection of Cr(III) and Cr(VI). The detection limit of Cr(III) by the naked eye was as low as 2.0 μM. Interestingly, a much lower detection limit was found for Cr(VI) than that for Cr(III) (0.4 μM by the naked eye). In addition, Cr(III) and Cr(VI) were easily distinguished upon pretreatment with K2CO3. The feasibility of this technique was evaluated for the successful detection of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in tap water samples with good recoveries. The detection mechanism has been discussed via several techniques including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), FT-IR spectroscopy, zeta potential (ζ-potential) measurement, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...